1. The Great Wall of China:
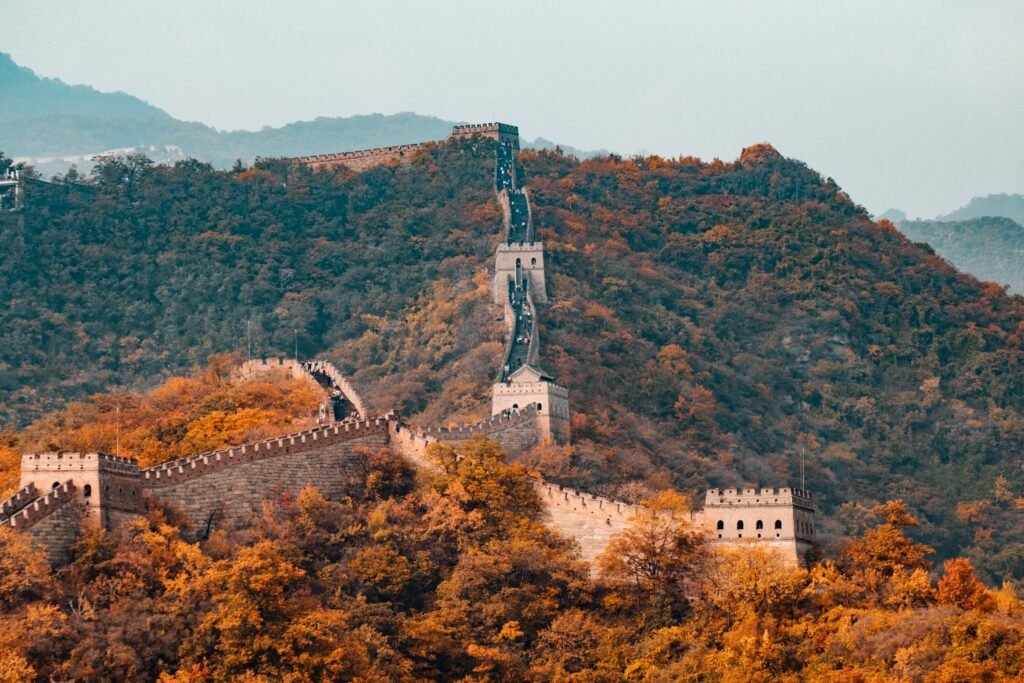

Location: China
History: Built over several dynasties, primarily during the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644).
Fame: The Great Wall is a symbol of China’s rich history and served as a defensive structure against invasions. It spans over 13,000 miles and is one of the most impressive architectural feats in history.
2. The Pyramids of Giza:
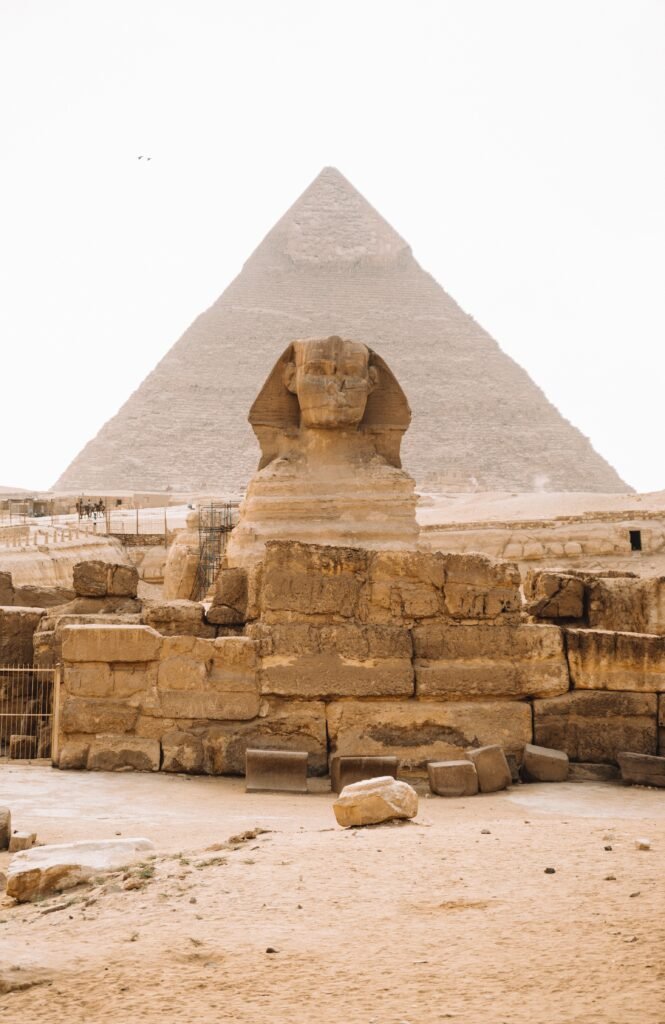

Location: Egypt
History: Built during the reign of Pharaohs in ancient Egypt, around 2580–2560 BCE.
Fame: The Pyramids, particularly the Great Pyramid of Giza, are marvels of ancient engineering. They were built as tombs for pharaohs and are a testament to the advanced knowledge and skills of the ancient Egyptians.
3. The Acropolis:
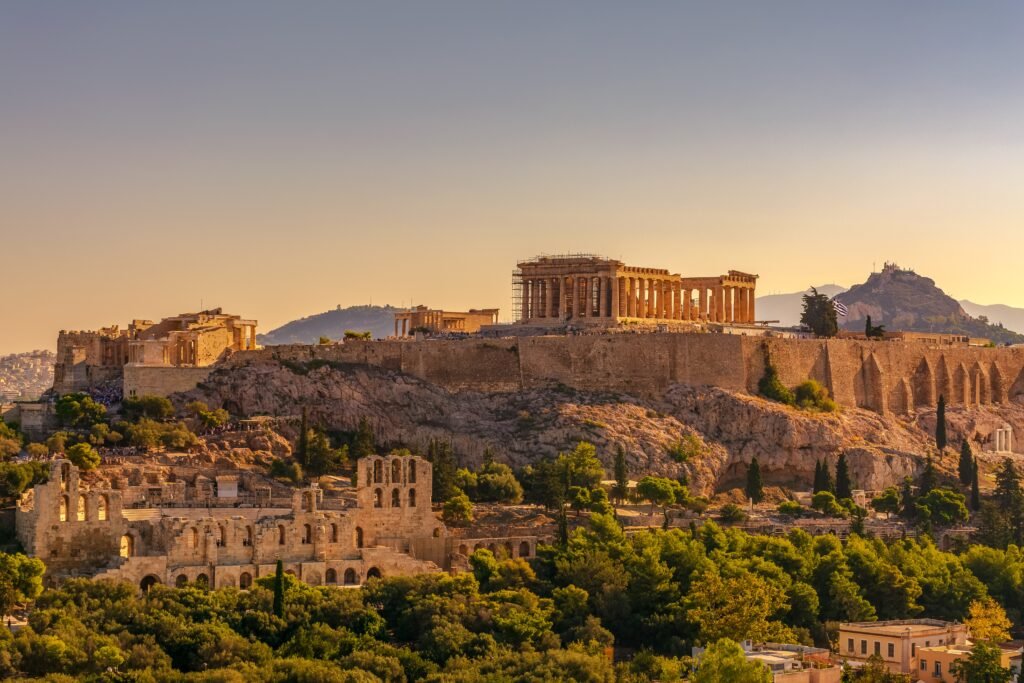

Location: Athens, Greece
History: Construction began in the 5th century BCE.
Fame: The Acropolis is a complex of ancient buildings, the most famous being the Parthenon. It’s a symbol of ancient Greek civilization, dedicated to the goddess Athena, and represents the pinnacle of classical Greek art and architecture.
4. Machu Picchu:

Location: Peru
History: Built by the Inca Empire in the 15th century.
Fame: Machu Picchu is an ancient Incan city located high in the Andes. Its breathtaking location and well-preserved ruins make it one of the most iconic archaeological sites, offering insight into Incan culture and engineering.
5. The Colosseum:

Location: Rome, Italy
History: Completed in AD 80 under Emperor Titus.
Fame: An ancient amphitheater, the Colosseum hosted gladiator contests and public spectacles. It is a symbol of Roman engineering and remains one of the most iconic structures of ancient Rome.
6. Taj Mahal:
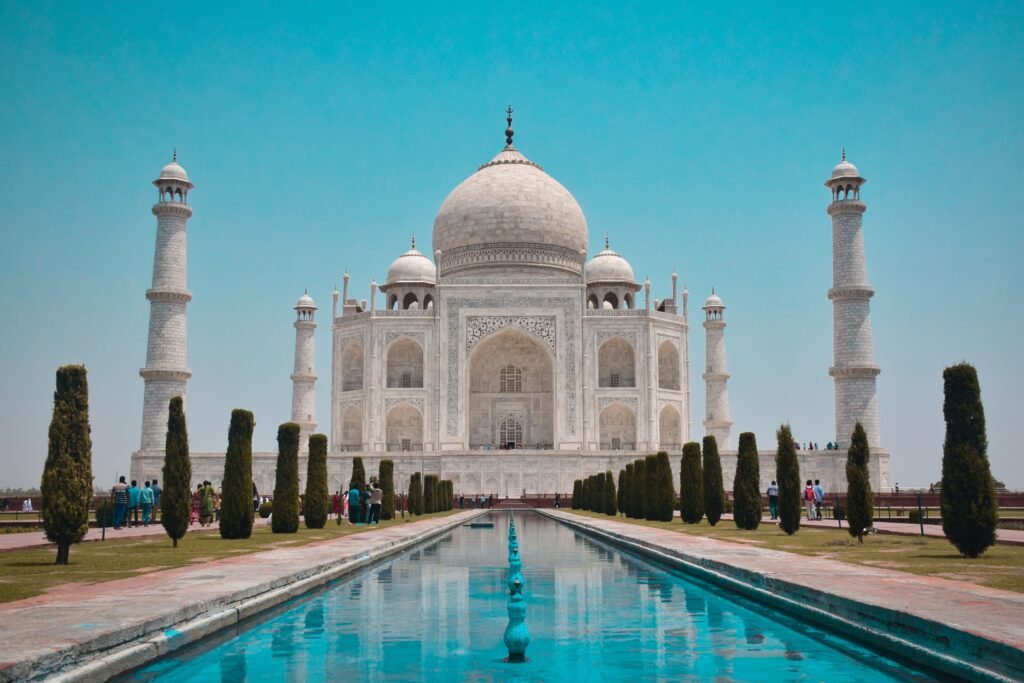

Location: Agra, India
History: Built in the 17th century by Emperor Shah Jahan.
Fame: The Taj Mahal is a masterpiece of Mughal architecture, constructed as a mausoleum for the emperor’s wife. Its stunning white marble structure and intricate details make it a symbol of love and one of the most recognized buildings globally.
7. Petra:
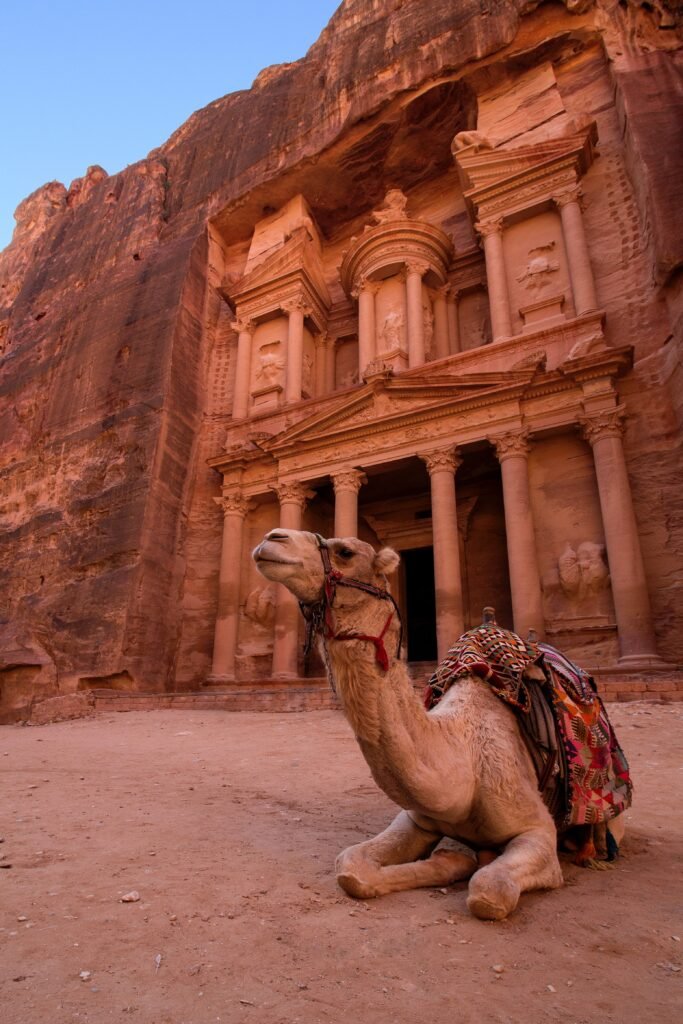

Location: Jordan
History: Established possibly as early as 312 BC.
Fame: Often referred to as the “Rose City” due to the color of the stone, Petra is an ancient city carved into the rose-red cliffs of southern Jordan. It was a thriving trading hub and the capital of the Nabataean Kingdom, highlighting remarkable rock-cut architecture.
8. Angkor Wat:
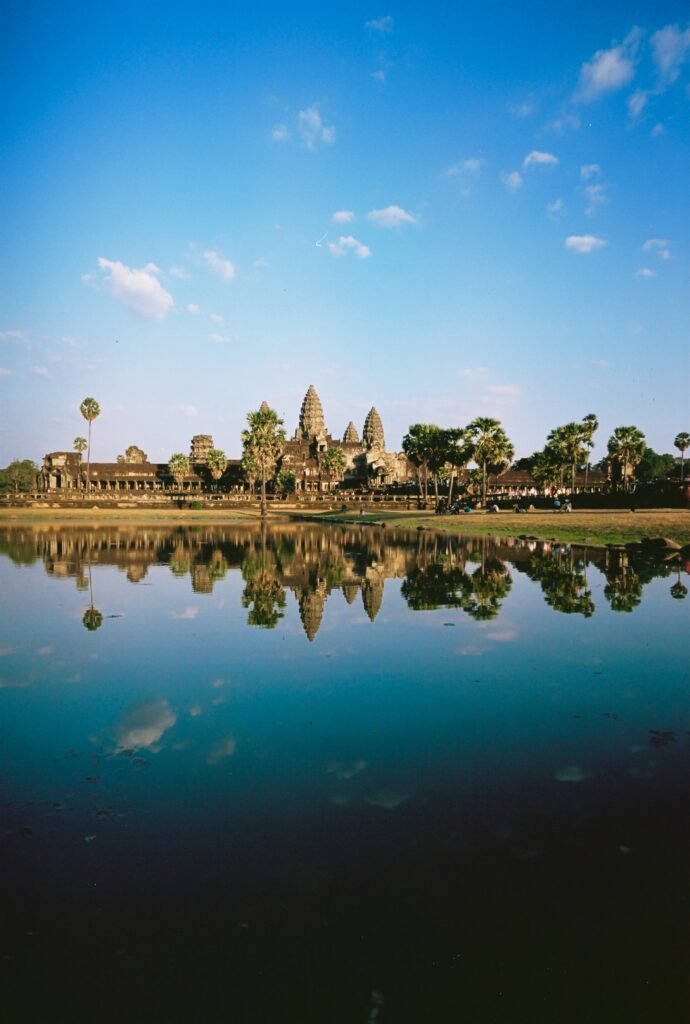

Location: Cambodia
History: Built in the 12th century by King Suryavarman II.
Fame: Angkor Wat is the largest religious monument globally, originally dedicated to the Hindu god Vishnu and later converted to a Buddhist temple. The intricate carvings and vast complex reflect the grandeur of the Khmer Empire.
9. The Alhambra:
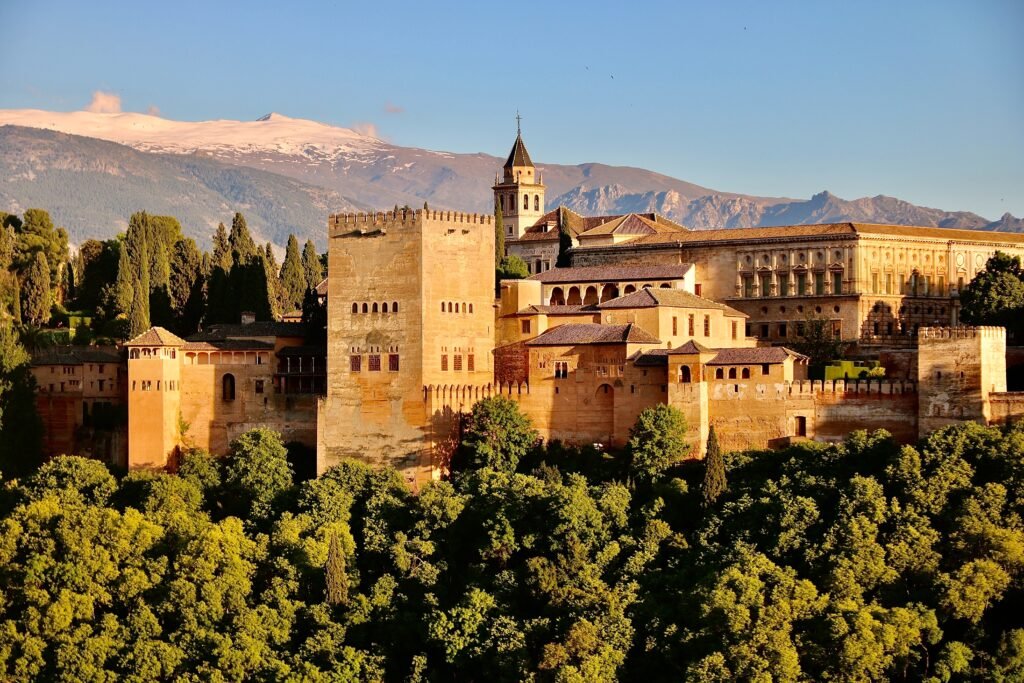

Location: Granada, Spain
History: Originally built in the mid-13th century.
Fame: A stunning palace and fortress complex, the Alhambra is a masterpiece of Moorish architecture. Known for its intricate tilework, arches, and beautiful gardens, it reflects the cultural richness of Islamic Spain.
10. The Forbidden City:

Location: Beijing, China
History: Completed in 1420 during the Ming Dynasty.
Fame: Also known as the Palace Museum, the Forbidden City served as the imperial palace for almost 500 years. It is a vast complex with over 9000 rooms and is a prime example of traditional Chinese palatial architecture.
11. Stonehenge:
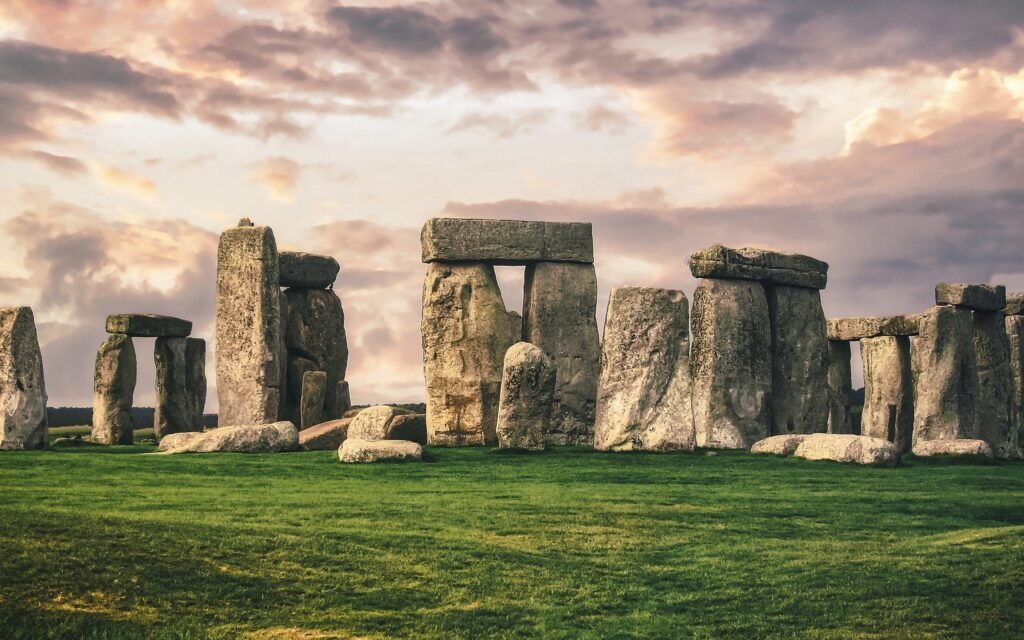

Location: Wiltshire, England
History: Construction started around 3000 BCE.
Fame: Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument with a ring of standing stones, each around 13 feet high, seven feet wide, and weighing around 25 tons. Its purpose remains a subject of debate, with theories ranging from an ancient burial site to an astronomical observatory.
12. Ephesus:

Location: Turkey
History: Founded in the 10th century BCE.
Fame: Once a flourishing Greek city and later a major Roman city, Ephesus is known for its well-preserved ancient ruins, including the Library of Celsus and the Great Theatre.
These historical places offer glimpses into the rich tapestry of human civilization, highlighting the creativity, ingenuity, and cultural diversity of societies across different eras and continents. Each site has a unique story to tell, contributing to the collective heritage of humanity.